Traits
Roan (Common)



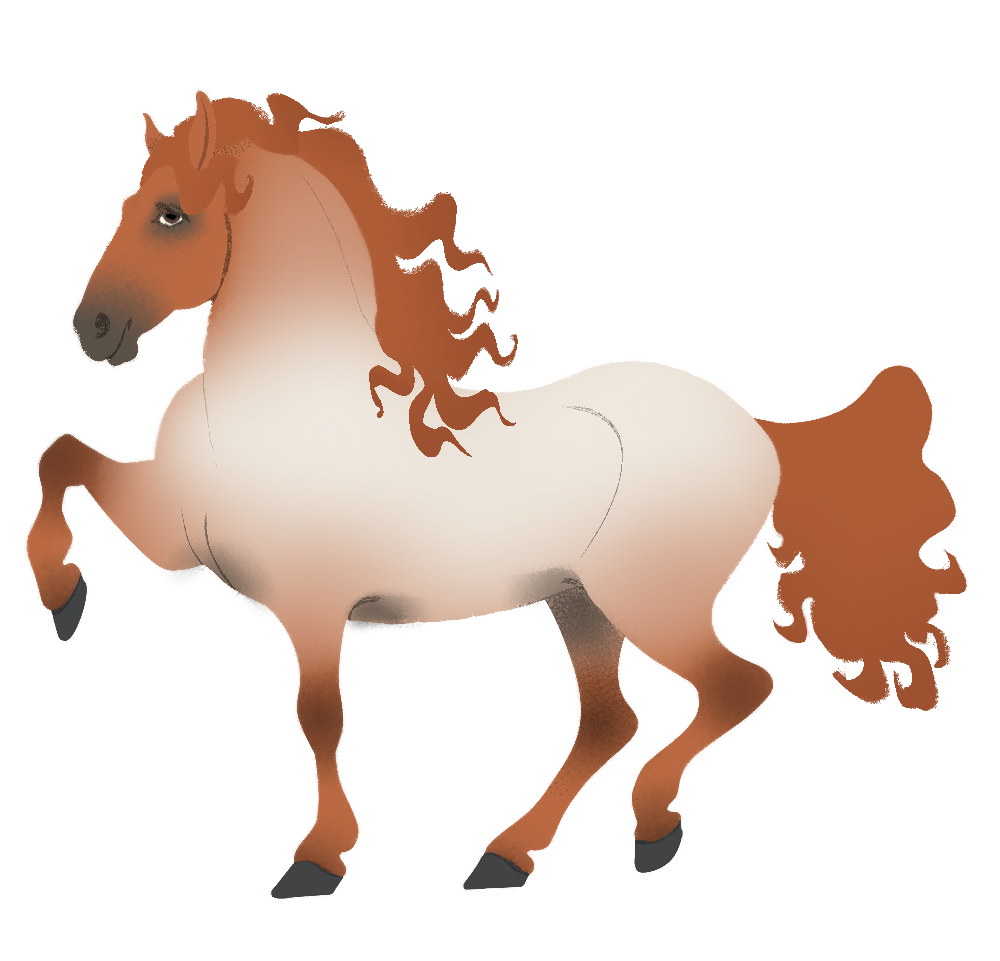
Roan is a lightening of the coat visible on the horse's barrel.
It may cause a light, grayish appearance compared to the base color or turn the coat nearly white.
"Corn Marks" may form in places where the horse's skin was damaged and healed with the base coat color showing through.
Roan should fade gradually into the base color at its edges.
Genotype: Rn_
Locus: Roan is a KIT gene mutation, along with Tobiano, Sabino, and Dominant White. A horse may carry only two KIT gene mutations.
- Coat: Roan is a white marking.
- Mane and Tail: Not affected.
- Skin: Not affected.
- Eyes: Not affected.
- Hooves: Not affected.
Range:
- Minimum: Visible lightening of base coat on top of the hindquarters.
- Maximum: Near-white lightening of the barrel and neck, with the base coat color visible above the horse's jaw and below the knees/hocks.
Interactions:
- Blanched: When Blanched and Roan are both present, Roan may be hidden.
- Filigree: Filigree and Roan do not interact.
- Chestnut: When Roan is on a Chestnut base coat, the phenotype will read "Red Roan."
- Black: When Roan is on a Black base coat, the phenotype will read "Blue Roan."

 Example art by
Example art by 
